When it comes to your health, having access to quality healthcare is essential. Healthcare systems refer to a complex network of organizations, institutions, and resources that work together to provide medical care to individuals and communities. The goal of a healthcare system is to improve the health outcomes of the population it serves while ensuring that care is accessible, affordable, and equitable.
The healthcare system in your country may vary depending on factors such as government policies, economic conditions, and cultural norms. Some countries have a universal healthcare system where everyone has access to medical care regardless of their ability to pay. Other countries have a mixed system where the government provides some aspects of healthcare while private entities offer others. Irrespective of the type of healthcare system, the ultimate goal is to provide high-quality care that meets the needs of the population it serves.

Healthcare Systems Overview
Individuals must have a basic understanding of the healthcare system. Healthcare systems are complex and vary from country to country, but they all share the same goal of providing quality care to patients. In this section, we will give you an overview of the critical components of the healthcare system and global perspectives.
Key Components
The healthcare system consists of various entities working together to provide patient care. These entities include healthcare providers, insurance companies, government agencies, and patients. Healthcare providers have doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and other medical professionals who care for patients. Insurance companies offer coverage for medical expenses and help patients pay for their healthcare. Government agencies regulate the healthcare system and provide funding for healthcare programs. Patients are the individuals who receive care from healthcare providers and use insurance to pay for their medical expenses.
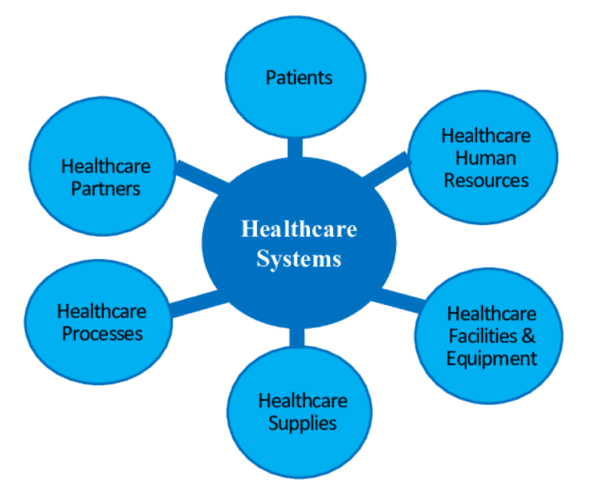
The US healthcare system comprises both public and private entities. Most Americans have private insurance, while two major federal government health insurance programs, Medicare and Medicaid, provide coverage for seniors and some disabled and healthcare services for some people experiencing poverty and near-poor, respectively. The US healthcare system is one of the most expensive in the world, with per capita spending far exceeding the OECD average.
Global Perspectives
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines health systems as “all organizations, people, and actions whose primary intent is to promote, restore, or maintain health.” Healthcare systems around the world vary in terms of their structure, financing, and organization. In some countries, such as Canada and the United Kingdom, healthcare is provided by the government and is free at the point of use. In other countries, such as Germany and Japan, healthcare is provided by a mix of public and private entities.
The development of healthcare systems is a crucial indicator of a country’s development. Countries with well-developed healthcare systems tend to have better health outcomes and a higher quality of life. The WHO works with countries worldwide to improve their healthcare systems and promote universal health coverage.

Healthcare systems are complex and consist of various entities working together to provide patient care. The United States healthcare system is a mix of public and private entities, while healthcare systems worldwide vary in structure, financing, and organization. The development of healthcare systems is a crucial indicator of a country’s level of development, and the WHO works with countries around the world to improve their healthcare systems and promote universal health coverage.
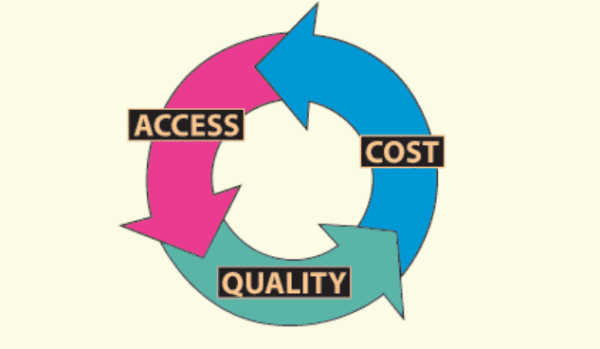
Access and Quality of Care
Access to healthcare and quality of care are two critical components that affect overall health. Access to healthcare refers to receiving timely and affordable medical care. Quality of care refers to the level of medical treatment received, including its effectiveness and outcomes.
Primary Care
Primary care is often the first point of contact for patients seeking medical care. Primary care providers include family practitioners, paediatricians, and internal medicine doctors. They provide preventative care, diagnose and treat illnesses, and manage chronic conditions. Access to primary care is essential for maintaining good health and preventing serious health problems.
Specialized Services
Specialized services refer to medical care specialists such as cardiologists, neurologists, and oncologists provide. These providers have advanced training in specific areas of medicine and can treat complex medical conditions. Access to specialized services is essential for patients who require specialized care for their health conditions.
Healthcare Equity
Healthcare equity refers to fair and equal access to healthcare services for all patients, regardless of their background or socioeconomic status. Lack of access to healthcare services can result in poorer health outcomes, and healthcare equity is critical for ensuring that all patients receive the care they need to maintain good health.
Insurance coverage is a critical factor in ensuring access to healthcare services. Without insurance coverage, patients may be unable to afford medical care or may be forced to delay necessary medical treatment. Healthcare providers can improve access to care by offering affordable payment options and working with insurance providers to ensure patients have access to the care they need.
Access and quality of care are critical components of the healthcare system. By ensuring that patients have access to timely and affordable medical care and high-quality medical treatment, healthcare providers can help patients maintain good health and prevent serious health problems.
Healthcare Economics
Healthcare economics is a branch of economics that studies the healthcare system, its costs, and how it is financed. This section will discuss the different aspects of healthcare economics, including fees and spending, insurance and coverage, and government and private payers.
Costs and Spending
The high cost of healthcare is a significant concern for many people. According to a Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services report, healthcare spending in the United States reached $3.8 trillion in 2019, about $11,582 per person. This high cost of healthcare is due to several factors, including the ageing population, advances in medical technology, and the high cost of prescription drugs.
Insurance and Coverage
Health insurance is a critical component of the healthcare system. It provides financial protection to individuals and families in case of illness or injury. Several types of health insurance include private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid. Personal insurance is typically provided by employers or purchased directly by individuals. Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance to people over 65. Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health insurance to low-income individuals and families.
Government and Private Payers
The government and private payers play critical roles in the healthcare system. The government is the largest payer of healthcare services in the United States through programs such as Medicare and Medicaid. Private payers, such as health insurance companies, also play an essential role. They negotiate prices with healthcare providers and pay for healthcare services on behalf of their members.
There has been a growing interest in price controls to control healthcare costs in recent years. Price controls can take many forms, such as government regulation of drug prices or limits on how much healthcare providers can charge for services.
Healthcare economics is a complex and multifaceted field critical to understanding the healthcare system. By understanding costs and spending, insurance and coverage, and government and private payers, one can better understand how the healthcare system works and how it can be improved.
Public Health and Prevention
As you explore the healthcare system, you’ll find that public health and prevention are crucial in keeping you healthy. Preventive care is essential in healthcare, focusing on maintaining good health, preventing chronic diseases, and detecting health problems early.
Disease Prevention
Prevention is one of the most essential pillars of public health. According to the Institute of Medicine (IOM), missed prevention opportunities cost the US $55 billion annually. Preventive care services can help to reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. Regular cancer screenings and vaccinations are the most effective ways to prevent diseases.
In addition to regular check-ups, lifestyle changes can also help prevent chronic diseases. Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking are all effective ways to reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases.
Health Promotion
Health promotion is another important aspect of public health. It focuses on creating a healthy environment that supports healthy behaviours. This can include policies that promote healthy eating, physical activity, and tobacco cessation.
Population health is another critical area of focus in public health. It involves understanding and addressing the health needs of specific populations, such as children, older adults, and low-income individuals.
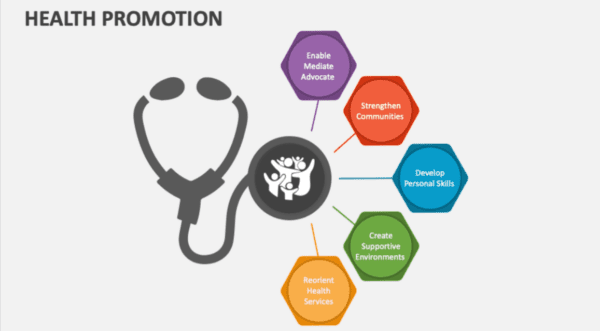
Overall, public health and prevention are essential components of the healthcare system. Individuals can maintain good health and reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases by focusing on prevention and health promotion.
Healthcare Delivery Systems
Regarding healthcare delivery systems, different types of facilities are available depending on your health needs. These facilities are designed to provide different levels of care to patients.
Hospitals and Acute Care
Hospitals are healthcare facilities that provide various services, including acute care, emergency care, and specialized care. Critical care is provided to patients requiring immediate medical attention for serious injuries or illnesses. Hospitals have technical departments such as cardiology, neurology, and oncology that provide specialized care.
Outpatient and Urgent Care
Outpatient and urgent care facilities provide medical care to patients who do not require hospitalization. Outpatient care is offered to patients who require medical attention but do not need to be admitted to a hospital, and urgent care centres treat minor injuries and illnesses that require immediate attention but are not severe enough to require hospitalization.

Long-Term and Palliative Care
Long-term and palliative care facilities treat patients who require ongoing medical attention. Long-term care is provided to patients who need assistance with daily living activities due to chronic illness or disability. Palliative care is offered to patients with severe disease who require pain management and symptom relief.
Nurses and other healthcare professionals are crucial in caring for patients in these healthcare delivery systems. Physicians and other providers work closely with nurses to ensure patients receive the best care possible.
Understanding the different types of healthcare delivery systems is vital to accessing the care needed when you need it. Whether you require acute care, outpatient care, or long-term care, facilities and professionals are available to provide it.
Challenges and Innovations
The healthcare system faces numerous challenges and innovations. Challenges include healthcare disparities, technological advancements, and policy and reform.
Healthcare Disparities
Healthcare disparities continue to be a significant challenge in the healthcare system. According to the IOM report, healthcare disparities are “differences in the quality of healthcare that are not due to access-related factors or clinical needs, preferences, and appropriateness of intervention ” and can be attributed to various factors such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and geographic location.
Technological Advancements
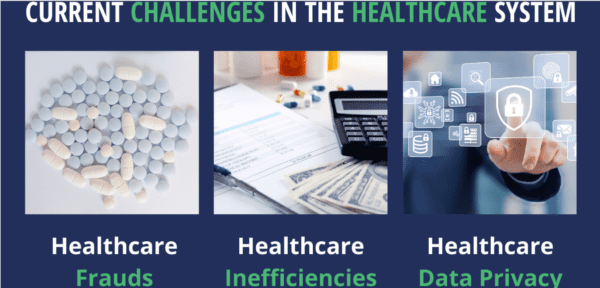
Technological advancements have revolutionized the healthcare industry. Innovations like telemedicine, electronic health records, and wearable devices have improved patient care and outcomes. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an increase in the use of telemedicine, allowing patients to receive care remotely. However, these advancements have also raised concerns about data privacy and security.
Policy and Reform
Policy and reform are crucial to addressing the challenges facing the healthcare system. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded access to healthcare for millions of Americans, but it has also faced criticism and challenges. Healthcare reform is necessary to address rising healthcare costs and mortality rates. Research and innovation play a crucial role in identifying and addressing these issues.
In conclusion, the healthcare system faces numerous challenges and innovations. Healthcare disparities, technological advancements, and policy and reform are just a few issues that must be addressed to improve patient care and outcomes. We can work towards a more equitable and efficient healthcare system through research and innovation.
