With the rise of digital tools and online learning platforms, EdTech data privacy and security become critical issues to address. EdTech, or educational technology, has revolutionized the way students learn and teachers teach as the education sector becomes increasingly reliant on technology. However, this dependence on technology has also raised concerns about data privacy and security.
As an EdTech user, it is important to understand the potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with digital learning tools. Your personal information, such as your name, email address, and even academic records, may be stored and processed by these platforms. Without proper safeguards in place, this information can be vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, or unauthorized access.
To ensure the safety and security of your data, it is crucial for EdTech companies to implement strong privacy and security measures. This includes using encryption to protect data in transit and at rest, regularly testing and updating security protocols, and providing transparent information about data collection and usage. By taking these steps, EdTech companies can help protect your personal information and ensure a safe and secure learning environment.
Understanding EdTech Data Privacy and Security
EdTech users ought to understand the types of data collected and how they are collected to ensure data privacy and security. This section will provide you with an overview of EdTech data, including the types of data collected and data collection methods.
Types of Data Collected
EdTech companies collect various types of data, including personal information, academic records, and behavioral data. Personal information includes student names, addresses, and contact information, while academic records contain grades, test scores, and attendance records. Behavioral data includes information on student behavior, such as their study habits, learning preferences, and engagement levels.
EdTech companies also collect metadata, which is data that describes other data. Metadata includes information on how students interact with educational content, such as the amount of time spent on a task, the number of attempts made, and the types of resources accessed.
Data Collection Methods

EdTech companies collect data through various methods, including:
- User Input: EdTech platforms may ask students to provide personal information, such as their name and email address, during the registration process.
- Cookies: EdTech platforms may use cookies to track user behavior and preferences.
- Analytics Tools: EdTech platforms may use analytics tools to collect data on user behavior, such as the number of clicks on a particular resource.
- Third-Party Services: EdTech platforms may use third-party services, such as Google Analytics, to collect data on user behavior.
It’s essential to note that EdTech companies must comply with data privacy laws, such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These laws regulate the collection, use, and disclosure of student data and provide students and parents with certain rights, such as the right to access and correct their data.
1. Legal Frameworks and Compliance in EdTech Data Privacy and Security
When it comes to EdTech data privacy and security, it is important to understand the legal frameworks and compliance requirements that govern the use and handling of student data. Below are some of the key regulations that educational institutions and EdTech companies must comply with.
FERPA
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is a federal law that protects the privacy of student education records. Under FERPA, schools must obtain written consent from parents or eligible students before disclosing any personally identifiable information (PII) from a student’s education record. This includes information such as grades, attendance records, and disciplinary records. FERPA also gives parents and eligible students the right to review and request changes to their education records.

EdTech companies that handle student data must also comply with FERPA. This means that they must have appropriate security measures in place to protect student data and must obtain written consent from schools or parents before using or disclosing any PII.
COPPA
The Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) is a federal law that governs the collection of personal information from children under the age of 13. COPPA requires websites and online services to obtain verifiable parental consent before collecting any personal information from children. This includes information such as name, address, email address, and phone number.
EdTech companies that collect personal information from children must comply with COPPA. This means that they must obtain verifiable parental consent before collecting any personal information and must have appropriate security measures in place to protect that information.
GDPR in Education
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European Union (EU) regulation that governs the collection, use, and storage of personal data. While GDPR is a European regulation, it applies to any organization that processes the personal data of EU citizens. This includes educational institutions and EdTech companies that collect personal data from EU citizens.
Under GDPR, individuals have the right to access their personal data, have that data corrected or erased, and object to the processing of their data. Organizations that collect personal data must also have appropriate security measures in place to protect that data.
Concerning EdTech privacy and security, GDPR applies to the processing of personal data of students, parents, and staff. This includes information such as grades, attendance records, and disciplinary records. Educational institutions and EdTech companies that collect personal data from EU citizens must comply with GDPR. This means that they must obtain consent from individuals before collecting their personal data and must have appropriate security measures in place to protect that data.

Overall, compliance with these legal frameworks is essential for ensuring the EdTech data privacy and security of student data. By understanding and complying with these regulations, educational institutions and EdTech companies can protect the sensitive information of students and their families.
2. EdTech Data Privacy and Security Policies
Protecting student data is of utmost importance as we increasingly use technology in the classroom. Hence, EdTech companies need to be transparent about their data collection and usage practices. This section explores some key aspects of EdTech data privacy and security policies.
Creating a Privacy Policy
A privacy policy is a legal document that outlines an EdTech company’s data collection, storage, and usage practices. It’s important to note that privacy policies are not one-size-fits-all and should be tailored to the specific needs of the company. When creating a privacy policy, there are a few key elements that should be included:
- Data Collection: The privacy policy should clearly state what data is being collected and how it’s being collected. This includes information such as name, email address, IP address, and browsing history.
- Data Usage: The privacy policy should explain how the collected data will be used. This includes whether the data will be shared with third parties, used for marketing purposes, or used to improve the product.
- Data Security: The privacy policy should outline the measures taken to protect the data from unauthorized access, theft, or loss. This includes encryption, firewalls, and access controls.
- Policy Changes: The privacy policy should state how changes to the policy will be communicated to users and when the policy will be updated.
Policy Enforcement
Creating a privacy policy is only the first step. When it comes to EdTech data privacy and security, companies in the space need to enforce their policies to ensure that student data is protected. This includes:
- Employee Training: All employees should be trained on the company’s privacy policy and understand the importance of protecting student data.
- Data Access Controls: Access to student data should be limited to only those who need it to perform their job duties.
- Third-Party Vetting: EdTech companies should vet third-party vendors to ensure that they have strong data privacy policies in place.
- Data Breach Response Plan: EdTech companies should have a plan in place in case of a data breach. This includes notifying affected parties, investigating the breach, and taking steps to prevent future breaches.

From the above perspectives, EdTech data privacy and security policies are crucial. EdTech companies need to be transparent about their data collection and usage practices and enforce their policies to protect student data. By following best practices and staying up-to-date with regulations, these companies can ensure that they are providing a safe and secure learning environment for students.
3. Data Privacy and Security Measures for EdTech Platforms
Since EdTech data privacy and security have become major concerns, EdTech platforms must take necessary measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of student and teacher data. Here are some data privacy and security measures that the existing diverse EdTech platforms should implement:
Encryption Techniques
Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. Strong encryption techniques should be used to protect data in transit and at rest. This includes encrypting data stored on servers, as well as data transmitted over the internet. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a widely accepted encryption standard that is recommended for protecting sensitive data.
Access Controls
Access controls are measures to restrict access to data to authorized personnel only. EdTech platforms should implement strong access controls to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This includes multi-factor authentication, password policies, and role-based access controls. It is important to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data and that access is granted on a need-to-know basis.
Regular Audits

Regular audits should be conducted to ensure that security measures are effective and up-to-date. This includes vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and security audits. Audits should be conducted by third-party security experts to ensure that there are no biases or conflicts of interest. Regular audits help identify security gaps and weaknesses and allow for timely remediation.
4. EdTech Data Privacy and Security Risk Management
As with any technology, EdTech solutions come with inherent risks that must be managed to ensure the privacy and security of student data. To effectively manage these risks, it is important to identify vulnerabilities and establish an incident response plan.
Identifying Vulnerabilities
The first step in managing EdTech data privacy and security risks is to identify potential vulnerabilities. This includes examining the security features of the EdTech solution, such as encryption and access controls, as well as assessing the data privacy policies of the provider. It is important to ensure that the EdTech solution aligns with your district’s data privacy policies and complies with relevant regulations such as FERPA and COPPA.
Another important consideration is the potential for data breaches through third-party integrations. Many EdTech solutions rely on third-party applications for functions such as authentication or analytics. It is important to ensure that these integrations have appropriate security measures in place and are compliant with data privacy regulations.
Incident Response Planning
In the event of a data breach or other security incident, it is important to have an incident response plan in place. This plan should include clear protocols for identifying and containing the breach, notifying affected parties, and conducting an investigation to determine the cause and extent of the breach.
It is also important to have a communication plan in place to notify parents, students, and other stakeholders of the breach and the steps being taken to address it. This communication should be transparent and timely to help rebuild trust in the district’s EdTech data privacy and security practices.
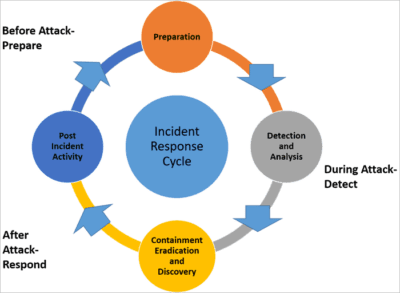
By identifying vulnerabilities and establishing an incident response plan, districts and schools can effectively manage the risks associated with EdTech solutions and ensure the privacy and security of student data.
5. EdTech Data Privacy and Security Ethical Considerations
As EdTech becomes more ubiquitous in classrooms, it is important to consider the ethical implications of collecting and using student data. While data can be used to improve learning outcomes and personalize instruction, it also raises concerns about privacy and security. In this section, we will explore some ethical considerations surrounding EdTech data privacy and security.
Student Data Rights
Students have the right to privacy and control over their own data. EdTech companies and schools need to be transparent about what data is being collected, how it is being used, and who has access to it. Students should also have the ability to access, correct, and delete their own data.
To protect student data privacy, adherence to regulations such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) and the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) is needed. These laws outline the rights of students and their families regarding the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information by educational institutions and companies.
Balancing Innovation and Privacy
While EdTech has the potential to revolutionize education, it is important to balance innovation with privacy and security concerns. EdTech data privacy and security should be a priority for companies in the industries, showcased in their product design and development. They should also conduct regular audits and risk assessments to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.

Schools and educational institutions should also prioritize EdTech data privacy and security when selecting and implementing EdTech tools. They should conduct thorough evaluations of products and services to ensure they meet privacy and security standards, and provide training to teachers and staff on best practices for protecting student data.
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are becoming increasingly important in the field of EdTech. These technologies have the ability to personalize learning experiences and provide students with real-time feedback. AI and machine learning can also help educators identify areas where students may be struggling and provide targeted interventions.
One application of AI and machine learning in EdTech is the use of chatbots. Chatbots can provide students with instant support and answer their questions in real time. This technology can also be used to create virtual tutors, which can provide students with personalized learning experiences. While the adoption of the trend continues, an awareness of EdTech data privacy and security issues and solutions is essential for schools and companies implementing these technologies.
Blockchain in Education
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way that education is delivered and managed. This technology can be used to create secure, tamper-proof records of student achievements and credentials. This can provide students with a more secure and portable way to showcase their skills and knowledge.

Blockchain technology can also be used to create decentralized learning platforms. These platforms can provide students with access to a wider range of educational resources and can enable them to earn credentials that are recognized across different institutions.
Overall, all current and emerging technologies that have the potential to transform the field of education must be implemented with caution due to potential EdTech data privacy and security issues. As these technologies continue to evolve, it will be important to ensure that they are used in a way that complies with EdTech data privacy and security laws and regulations.
