Inclusive learning in edtech is a crucial component of a modern and equitable education system that is accessible to all. Inclusive learning in edtech focuses on creating a supportive environment where every student feels valued and respected. Accessible education aims to provide equal opportunities for all students, regardless of their abilities, by removing barriers that prevent them from fully engaging in the learning process.

Inclusive education is based on the principles of respect, diversity, and equity. It recognizes that every student is unique and has different learning needs. By providing a supportive environment that values diversity, inclusive education helps students to develop a sense of belonging and self-esteem. Inclusive education also recognizes that some students may require additional support to fully participate in the learning process.
Despite the benefits of inclusive education, there are still many barriers that prevent students from fully engaging in the learning process. These barriers can include physical, social, and cultural factors. Physical barriers may include inaccessible buildings or classrooms. Social barriers may include discrimination or bullying. Cultural barriers may include language or cultural differences.
Key Takeaways
- Inclusive learning and accessible education are crucial components of a modern and equitable education system.
- Inclusive education is based on the principles of respect, diversity, and equity.
- Despite the benefits of inclusive education, barriers such as physical, social, and cultural factors still prevent students from fully engaging in the learning process.
1. Principles of Inclusive Education
Inclusive education involves creating an environment where every student feels valued and supported, regardless of their background or abilities. To achieve this, educators must embrace a set of principles that promote equity, diversity, and accessibility in the classroom. Here are some of the key principles of inclusive education:
Universal Design for Learning
One essential principle of inclusive learning in edtech is Universal Design for Learning (UDL). UDL is an approach to teaching that aims to make learning accessible to all students. It involves creating multiple pathways for students to engage with the material, such as providing different formats for content, offering various ways to demonstrate learning, and providing options for student engagement.
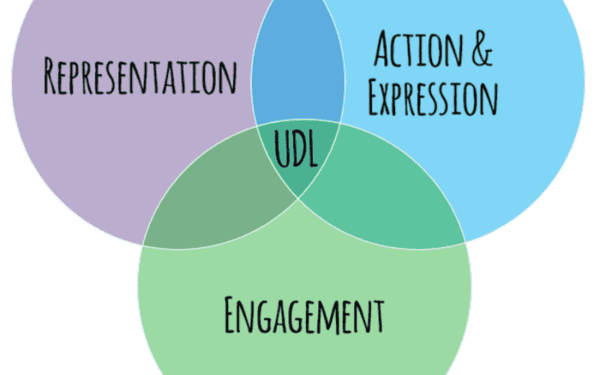
UDL is based on the idea that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to teaching and learning. By incorporating UDL principles, educators can create a learning environment that is flexible and responsive to the needs of all students.
Differentiated Instruction
Another key principle of inclusive education is differentiated instruction. Differentiated instruction involves tailoring instruction to meet the needs of individual students. This can include providing different levels of support, using varied instructional strategies, and offering different types of assessments.
By using differentiated instruction, educators can ensure that all students are challenged and engaged in the learning process. This approach recognizes that students come to the classroom with different backgrounds, experiences, and abilities, and it seeks to provide a learning experience that is tailored to each student’s needs.
Equity and Diversity in the Classroom
Inclusive education also involves promoting equity and diversity in the classroom. This means creating a learning environment that is welcoming and supportive of all students, regardless of their race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, or ability.
To achieve this, educators must be aware of their own biases and work to create a classroom culture that is inclusive and respectful of all students. This can include using diverse materials and resources, such as emerging educational technologies, promoting inclusive language, and creating opportunities for students to share their own experiences and perspectives.
These principles of inclusive education are designed to create a conducive learning environment for all students. By embracing these principles, educators can help to ensure that every student has the opportunity to succeed and thrive in the classroom.
2. Barriers to Inclusive Education
Inclusive education is about ensuring that all students, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, have equal access to education. However, there are many barriers that prevent students with disabilities from accessing education on an equal basis with their peers. Some of the most common barriers to inclusive education include:
Physical and Technological Barriers
Physical and technological barriers can make it difficult or impossible for students with disabilities to access education. For example, inaccessible buildings, classrooms, and transportation can prevent students with mobility impairments from attending school. In addition, a lack of accessible technology, such as screen readers or captioning, can make it difficult for students with visual or hearing impairments to access educational materials.
Social and Attitudinal Barriers
Social and attitudinal barriers can also prevent students with disabilities from accessing education. Stigma and discrimination can create negative attitudes towards students with disabilities, which can lead to bullying and exclusion. Teachers and other school staff may also have negative attitudes towards students with disabilities, which can lead to lower expectations and less support for these students.
Policy and Regulatory Challenges
Policy and regulatory challenges can also create barriers to inclusive education. Some countries may not have laws or policies in place to ensure that students with disabilities have equal access to education. In addition, even when laws and policies are in place, they may not be enforced effectively.
For instance, the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and the Americans with Disabilities Act both require that schools provide reasonable accommodations for students with disabilities, but some schools may fail to do so. Similarly, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act requires that schools provide accommodations for students with disabilities, but some schools may not be aware of this requirement or may not know how to implement it effectively.

In order to ensure that all students have equal access to education, it is important to address these barriers and create an inclusive learning environment that is accessible to all students. This may require changes in attitudes, policies, and practices, as well as investments in physical and technological infrastructure. By working together to address these challenges, we can create a more inclusive and equitable education system for all students.
3. Strategies for Accessible Learning
As an educator, it is your responsibility to ensure that all students have access to learning materials and experiences. This means providing accommodations, assistive technologies, and accessible learning materials. Here are some strategies you can use to make your classroom more inclusive.
Curriculum Adaptation and Accommodations
Curriculum adaptation and accommodations are essential for ensuring that all students have access to the same learning opportunities. Some strategies you can use include:
- Providing alternative formats for instructional materials, such as audio or braille.
- Using universal design principles to create accessible learning materials.
- Offering extended time for assignments and assessments.
- Providing note-taking services or allowing the use of assistive technology for note-taking.
Assistive Technologies and Resources
Assistive technologies and resources can help students with disabilities access learning materials and participate in classroom activities. Some examples include:

- Screen readers and text-to-speech software.
- Speech recognition software.
- Braille displays and refreshable braille devices.
- Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices.
Teaching Practices and Teacher Training
Teaching practices and teacher training are also important for creating an inclusive classroom. Here are some strategies you can use:
- Encourage student participation and engagement.
- Use clear and concise language.
- Provide opportunities for collaborative learning.
- Attend workshops and training sessions on inclusive teaching practices.
By implementing these strategies, you can create a more accessible and inclusive learning environment for all students. Remember, it is important to continually evaluate your teaching practices and make adjustments as needed to ensure that all students have access to the same learning opportunities.
4. Engagement and Participation
Inclusive education’s primary goal is to ensure that all students have access to the same learning opportunities. Engaging students in the learning process is key to achieving this goal. Here are some ways to foster student engagement:
Fostering Student Engagement
- Provide opportunities for students to collaborate with one another. Group work can be an effective way to get students engaged in their learning and help them develop important social skills.
- Use a variety of instructional methods to keep students interested and engaged. This could include using multimedia resources, hands-on activities, or real-life examples.
- Encourage active participation in class discussions. This can help students develop critical thinking skills and gain confidence in expressing their ideas.
- Create a positive learning environment that is inclusive and welcoming to all students. This can help students feel more comfortable and engaged in their learning.

Family and Community Involvement
Engaging families and the broader community can also be an important part of creating an inclusive learning environment. Here are some ways to involve families and the community:
- Communicate regularly with families about their child’s progress and learning goals. This can help parents feel more involved and invested in their child’s education.
- Encourage families to participate in school events and activities. This can help build a sense of community and create opportunities for families to connect with one another.
- Partner with community organizations to provide additional resources and support for students and families. This can help create a more inclusive community that is invested in the success of all students.
Assessment and Feedback Mechanisms
Assessment and feedback are important tools for measuring student progress and ensuring that all students have access to the same learning opportunities. Here are some ways to create inclusive assessment and feedback mechanisms:
- Use a variety of assessment methods to ensure that all students have the opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge and skills. This could include written assessments, oral presentations, or project-based assessments.
- Provide timely and constructive feedback that is tailored to each student’s individual needs. This can help students understand their strengths and weaknesses and make progress toward their learning goals.
- Ensure that assessment and feedback mechanisms are accessible to all students, including those with disabilities or other special needs. This could include providing accommodations such as extra time or alternative formats for assessments.
By fostering student engagement, involving families and the community, and creating inclusive assessment and feedback mechanisms, you can help create a more inclusive learning environment that supports the success of all students.
5. Global Perspectives and Case Studies
International Education Models
Inclusive education is a global priority, and several international organizations are working towards providing marginalized communities with access to quality education. The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) is one such organization that has been working towards this goal. UNICEF has been instrumental in developing international education models that promote inclusive education. These models focus on creating an environment that is conducive to learning for all children, irrespective of their backgrounds.

Case Study: Kenya’s Inclusive Education
Kenya is one of the countries that has been working towards providing inclusive education to marginalized communities. The Kenyan government has put in place policies and programs that promote inclusive education. These policies and programs focus on providing access to education for all children, irrespective of their backgrounds.
Kenya’s inclusive education policy has been successful in increasing enrollment rates for marginalized communities. The policy has also led to the development of new teaching methods that cater to the needs of all students, including those with disabilities. The policy has also led to the development of new teaching materials that are accessible to all students.
In conclusion, international organizations and governments are working towards providing marginalized communities with access to quality education. The different dynamics involved show that the world has achieved significant milestones in attempts to foster inclusive learning. Many of the dynamics discussed include the integration of educational technologies (edtech), combined with policy regulations to guide the process.
